Digitalization has made its mark in every sub-domain of the healthcare sector, and the pharmacy industry is no exception. The advent of smart Pharmacy management systems has eased countless operational woes for pharmacy business owners. So, what is a pharmacy management system? Well, it’s a software system that has been programmed for carrying out various functions that are needed to operate a pharmacy business.
Versatile pharmacy software works wonders for pharmacy owners as well as consumers. A sound pharmacy solution automates and simplifies pharmaceutical functions like medication dispensing, identifying drug over-usage, etc. resulting in smart pharmacy management, reduced errors, and enhanced patient services.
Now the question that arises in your mind is; “What features to include in sound Pharmacy software?” This post provides you with detailed insights on the essential features to integrate within a modern-day pharmacy management software system. Let’s get started!
Pharmacy Management System: Essential Features
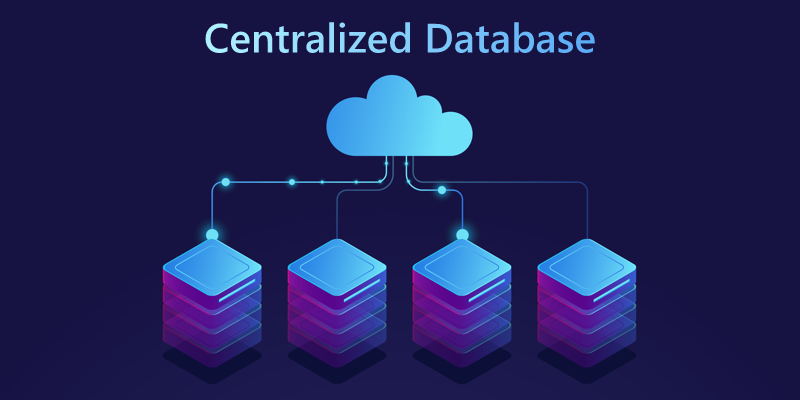
A Centralized Database for Data Storage
Data plays an important role in the pharmacy sector. Hence, a pharmacy business must ensure the safe and secure storage of data as well as a productive data processing mechanism. A pharmacy management system offers a centralized database for storing medicine-related data securely so that data is never lost and can be retrieved easily whenever needed. The system software also manages transaction records.
This feature adds to the patient’s convenience as it simplifies data search, ensures secure data access, and facilitates information collection about medicine availability. Providers reap the advantages of auto-generated drug reports, the need for a lesser workforce, improved communication between the pharmacy staff, real-time visibility into inventory and sales through advanced data analytics, and enhanced decision-making. The best part is that this centralized database is highly effective for businesses with small databases as well.
e-Prescription Generation
The usage of e-Prescriptions or electronic prescriptions is gaining momentum these days. Here’s how the process of e-prescribing functions?
A prescription is created electronically and then, transmitted from the prescriber to the pharmacy. Usually, a CPOE (computerized provider order entry) system like an EHR is employed for this purpose. The doctor creates a medication order using a CPOE system and sends it to the patient’s pharmacy through a secured connection. Once, the e-Prescription is generated, the pharmacy tracks the order and communicates whether that order was received and filled. Such communication between two systems is made possible with the usage of SCRIPT, a special XML-based standard. However, any type of prescription creation software needs to be Surescripts certified. So, healthcare entities generating ePrescriptions have to either get their system certified or pick pharmacy app development services that support Surescripts certification.
The e-Prescription feature saves paperwork, reduces the chances of human errors, and rules out the possibility of the prescription being lost or stolen. Moreover, as doctors can send medication refills directly to the pharmacy, medicines are speedily dispensed. Furthermore, patients availing of e-Prescription enjoy benefits like getting notified if they had missed picking up their order, creating order renewal requests with just a few clicks, and many more.
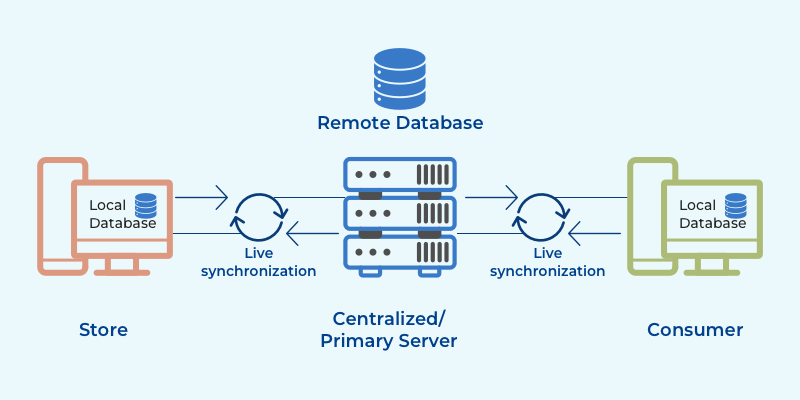
Synchronization with Real-time Information
An ideal pharmacy management system need to consider situations like technical glitches and system crashes where the data can get lost in a split of a second. For this reason, the system must synchronize with real-time data including price-related updates, inventory updates, and auto-program updates. This feature promotes real-time interaction and hence, allows pharmacists to help patients with insurance forms as well.
Analytics & Report Generation
Pharmacies interact with countless patients daily. This data concerning patient interaction is immensely beneficial as it helps pharmacy businesses in understanding the requirement, planning the future course of action, and improving business strategies. This data can also be useful while carrying out audits, inspections, or certification processes in the future.
A pharmacy app records data of each patient interaction, stores it in the pharmacy information system, and generates classified sales reports that are organized product-wise and category-wise. These reports calculate the factors that determine medication sales and provide crucial insights into the business activities of a pharmacy service. Service providers can effortlessly identify purchase patterns like which consumers frequently visit the pharmacy for medicine refills and what kind of medicines they order, which medicines are in demand at a particular season, etc. This way, pharmacy wholesalers/vendors can stock medicines as per the consumer requirement, be sufficiently equipped to handle the demand surge for specific drugs during a particular season like the flu season, and devise profitable marketing strategies.
Implementing an ERP system will help in handling monitoring & analysis activities and statutory audit checks.
Reports reveal a great deal about the current performance metrics of a pharmacy, the areas of improvement for boosting the ROI, and the budgeting roadmap that need to be followed. Data analytics reports also help pharmacy owners to detect suspicious patterns and check anomalies within their operations. Overall, reports lead to more informed decisions and increased revenues.
Necessary Integrations
An effective pharmacy management system must be able to integrate with other healthcare systems to facilitate the seamless flow and consistency of medical data. Let’s take a look at the commonest integrations needed. Interaction with a medical facility’s EHR enables the pharmacy solution to access the treatment records, as well as the medical history of patients, and integration with the logistics system helps in timely medicine distribution. Pharmacy software also needs to integrate with billing systems, hospital management systems (HMS), relevant external platforms, etc.
Dashboard
An in-built dashboard that provides actionable insights is of prime importance in a complex pharmacy management system. The presence of a dashboard helps pharmacy providers track the amount of medicines that are produced and the amount of wastage as well. Dashboards offer KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) through focused charts and reports. The KPI reports are based on the service provider’s key goals and display only those pieces of data that the pharmacy owner requires to fulfill a specific objective they have set. Therefore, this data not only boosts data analysis but also enhances business productivity and collaboration.
Support for SMS Alerts and Multi-store/Multi-location Management
The feature supporting SMS and notification allows pharmacists to get intimated whenever any patient’s medication is about to expire and they need a refill. Pharmacy staff then notifies patients via text messages before their prescriptions run out and patients can inform the pharmacist that they need a refill by just responding to the message received. Also, pharmacists can continuously stay in touch with consumers through status updates, thereby elevating the patient experience.
If pharmacy software offers multi-store and multi-location support, owners can manage the functioning of several stores at different locations. Pharmacy providers can view the exchange of electronic data concerning sales, returns, stock levels, etc., and also calculate the profits made by the entire pharmacy chain.
Medication Order Management
A pharmacy management system makes use of reordering points or the pharmacy-defined par levels for generating automatic orders. Thereafter, it calculates the number of items required for raising the stock level; it then adds the required quantity of items to the order. An EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) methodology is used for delivering the orders.
Managing Medication Expiries
Pharmacies suffer losses on account of expired drugs. Since pharmacies buy medication from whole sellers in bulk, every medicine has a different expiry date and MRP. Therefore, it becomes challenging for pharmacists to keep track of the expiry dates of each medicine. As a result, several drugs get expired while lying on the shelves of pharmacies without the knowledge of pharmacists and the pharmacy owners come to know about it only after the date of expiry, leading to medication wastage.
A pharmacy management system having the expiry management functionality notifies the owners about the expiry dates of medicines well in advance. This provides pharmacy owners the option to either sell those medicines to customers or return them back to the supplier. This way, wastage of medicines and financial losses can be avoided.
Management of Medication Re-ordering
The medication re-orders management feature provides critical insights that help pharmacists to stay informed and organized. Right from establishing re-order points, to finding out when to replenish the stock, and determining which product fares better in the inventory, this functionality does it all.
Pharmacists have to pre-define the maximum and minimum stock level margins, and then feed this data into the system. Now, the system alerts them whenever the stock level goes below the minimum point prompting them to reorder. It also suggests the best purchase option to the user, as per the programs offered by nearby suppliers, and recommends purchase schemes that offer super-saving options.
Module for User Management
A user management module helps pharmacy providers effortlessly set access-related preferences for different groups of users in order to reserve certain features for specific users. This includes restricting access to certain features for different audiences. The functions of this module can be segregated into two categories – Administrator User and Administrator Authentication User.
The Administrator User Module empowers the user to control the buying-selling process and carry out actions like viewing the medication stock available in the pharmacy; enlisting the medicines they need, tracking the pharmacy map, etc. This category of user management regulates the daily processing of stocks and sales.
The Administrator Authentication User Module allows the authenticated users to view every process including the transactions, sales reports, etc., manipulate the medication lists as well as stocks, track their everyday activities, and generate daily accounts using the multi-site software.
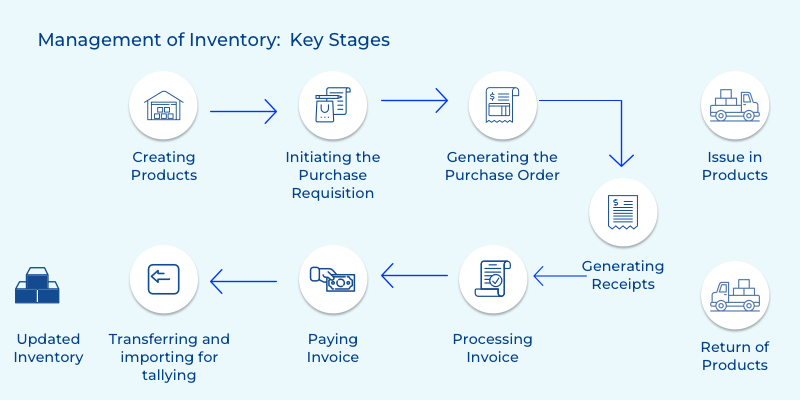
Inventory Management
The module for managing stocks in the inventory proves very handy to pharma owners. This feature integrates an EDI or APIs to order data. The offerings include classification of inventory products based on their categories, receiving as well as generating automatic orders, drug dispensing, managing out-of-stock products, and providing inventory counts and print labels. The software generates inventory reports that enable the suppliers and pharmacists to identify the best-selling products and figure out which drugs are affecting the distribution and ordering processes.
Sales Management Modules
Billing and accounting tasks in a pharmacy are often prone to errors. Nevertheless, an efficient pharmacy management system offering the sales management feature can optimize such tasks and eliminate the chances of errors. Here, the system automates the tasks of receiving orders, executing payments, and generating receipts; then add these tasks in reports.
The sales management module correctly matches the product codes to formulate their accurate prices, resulting in error-free billing. POS or point-of-sales module offers patients a wide range of options for making payments and completing returns.
Some billing modules offer electronic signatures and options for managing patient data and loyalties. And, if patient data is connected with billing histories, smart analytics utilizes this data for creating real-time financial reports and provides recommendations on improving patient experience.
Managing Prescriptions and Doctor Commissions
Difficulty in reading prescriptions by the patients and pharmacists has always been the source of confusion and errors in drug dispensing. The usage of a competent pharmacy management system resolves such woes as the data is directly entered by the doctor and electronically stored within the system.
The system also tracks pharmaceutical transactions to identify which practitioner has created a particular prescription or which medical representative is involved in a specific transaction with the pharmacy regarding medication sales. Such software instantly calculates the doctor/MR commission generated by the pharmacy for each medicine sold out and each prescription involved.
Compliance with Standard Regulations
Compliance with standard regulations mandated by authorities is essential for any pharmaceutical practice. So, a pharmacy management system must be compliant with the latest security practices and evaluation parameters mandated for activities like e-prescription generation, medication ordering, medicine refill, etc.
For instance, DSCSA (Drug Supply Chain Security Act) prohibits US pharmacies to dispense fake medicines and thus protects the citizens from counterfeit medication. Canadian pharmacies have to comply with the regulations defined by NAPRA and European pharma stores need to verify the authenticity of each medicine by employing a point-of-dispense validation system.
Bottomline:
I hope this post was informative and has given you a clear idea of which features to add while executing the pharmacy app development process. However, you need to pick the features as per your requirement and business objectives.
If you are a novice in the software development arena, it would be advisable to team up with skilled healthcare app developers or a reliable IT firm that has extensive experience in pharmacy app development. Your partner will take care of your pharmacy software development project right from app ideation to deployment.